What Are Benign Breast Conditions?
Most breast conditions are not cancer (benign), causing no serious harm to you. But all women are at some risk for breast cancer. Your risk increases as you grow older.
Common benign breast changes are covered here. Having one of these conditions does not put you at a higher risk for breast cancer. But all breast changes should be checked by a doctor to know what the change is and whether it should be treated.
Breast infection
Infections of the breast tissue can cause skin redness, warmth, and pain or tenderness. The most common infection is mastitis. This inflammation of the mammary glands can happen during breastfeeding. Mastitis and other breast infections are often treated with antibiotics.
Nipple discharge
Many women can squeeze a tiny amount of a clear or milky discharge from one or both nipples. This discharge may be normal. Other kinds of discharge may be symptoms of a breast condition. A dark or bloody discharge can be caused by a benign growth in a duct near the nipple (an intraductal papilloma). It should be checked by your doctor.
Fibrocystic changes
These benign changes may cause a thickening and firmness in the breasts. Breasts may be tender or painful. They may feel more dense in some areas than in others. Sometimes solid or fluid-filled lumps (cysts) may also form. Cysts may be smooth, soft or firm, and tender. They may become larger and more tender right before your period. An ultrasound may be done to make sure that a lump is a fluid-filled cyst and not cancer.
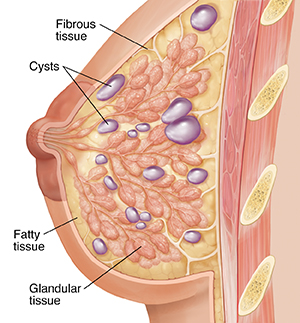
Benign breast lumps
Benign breast lumps come in all shapes, textures, and sizes. A lump of fibrous tissue (fibroadenoma) may be smooth, firm, and rubbery. This type of lump is usually painless and movable. Have any lump checked by your doctor.

Online Medical Reviewer:
Heather M Trevino BSN RNC
Online Medical Reviewer:
Janet Campbell RN BSN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Tennille Dozier RN BSN RDMS
Date Last Reviewed:
5/1/2025
© 2000-2026 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.