A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Topic IndexLibrary Index
Click a letter to see a list of conditions beginning with that letter.
Click 'Topic Index' to return to the index for the current topic.
Click 'Library Index' to return to the listing of all topics.
Anatomy and Function of the Heart's Electrical System
The heart's electrical system
The heart is a pump made up of muscle tissue. Like all muscles, the heart needs a source of energy and oxygen to work. The heart's pumping action is controlled by an electrical system. This system organizes how the chambers of the heart contract and pump blood.
How does the heart beat?
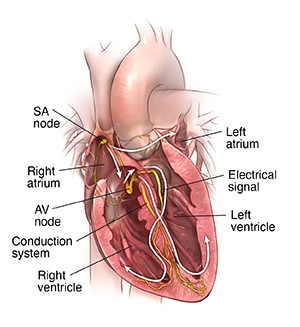
Normally, as the electrical impulse moves through the heart, the heart contracts about 60 to 100 times a minute. The rate depends on a person's age.
Each contraction of the ventricles is 1 heartbeat. The atria contract a fraction of a second before the ventricles. The blood in the atria empties into the ventricles. Then the ventricles contract.
An electrical signal starts in the sinus node of the heart. This is also called the sinoatrial node (SA node). This is a small area of special cells in the right upper chamber (atrium) of the heart. The SA node creates an electrical signal 60 to 100 times per minute. The 2 upper chambers of the heart (atria) are stimulated first and contract for a short period of time before the 2 lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). The electrical signal spreads through the chambers of the heart. First, the atria are activated. The electrical signal then travels down through the conduction pathways to the heart's ventricles. This causes them to contract and pump out blood.
The electrical signal then travels from the sinus node to the atrioventricular node (AV node). There, the signals slow down for a very short period. Then they continue down the conduction pathway through a small group of cells called the bundle of His. The bundle of His divides into right and left pathways. These are called bundle branches. They stimulate the right and left ventricles. The signal travels into the ventricles. This completes 1 heartbeat.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Callie Tayrien RN MSN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Stacey Wojcik MBA BSN RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Steven Kang MD
Date Last Reviewed:
8/1/2022
© 2000-2024 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.