A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Topic IndexLibrary Index
Click a letter to see a list of conditions beginning with that letter.
Click 'Topic Index' to return to the index for the current topic.
Click 'Library Index' to return to the listing of all topics.
Foot Surgery: Neuroma or Plantar Callus
Tight shoes and high heels can place extra pressure on the ball of your foot, causing neuromas and calluses. A neuroma is an inflamed nerve. It can cause pain, numbness, or burning. A plantar callus is a buildup of hard skin on the ball of the foot. The callus may feel like a stone in your shoe.
There are many nonsurgical treatments for neuromas and calluses. But if these are not helpful, surgery may be considered.
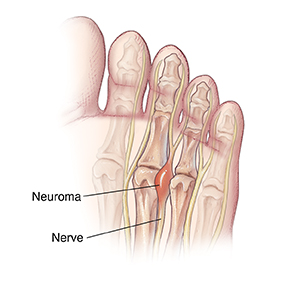
Neuroma
When 2 metatarsal bones are squeezed together, they may pinch the nerve that runs between them. The pinched nerve can become swollen and painful. This often happens at the base of the third and the fourth toes. Standing or walking for a while can increase the pain.
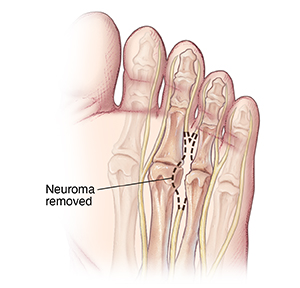
Neuroma removal
The enlarged part of the inflamed nerve is removed. Most often, you can bear weight on your foot right away. You may have to wear a surgical shoe for a few weeks. When healed, a small area may feel numb, where part of the nerve was taken out.
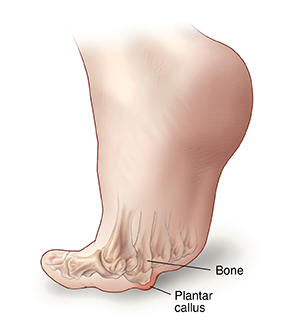
Plantar callus
When one metatarsal bone is longer or lower than the others, it presses on the skin beneath, forming a callus. Wearing shoes with thin soles and high heels can also place extra pressure on the ball of your foot. As a result, the callus may cause foot pain and irritation.
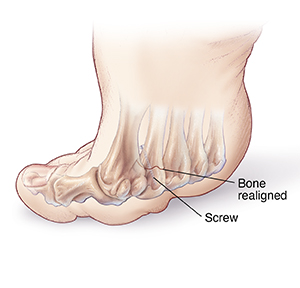
Bone removal
The affected metatarsal bone is cut and aligned with the other metatarsals (oblique osteotomy). Screws or pins may be used to hold the bone in place. Only part of the metatarsal bone is removed. The plantar callus should go away on its own over time.
Online Medical Reviewer:
L Renee Watson MSN RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Raymond Turley Jr PA-C
Online Medical Reviewer:
Thomas N Joseph MD
Date Last Reviewed:
11/1/2021
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.