A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Topic IndexLibrary Index
Click a letter to see a list of conditions beginning with that letter.
Click 'Topic Index' to return to the index for the current topic.
Click 'Library Index' to return to the listing of all topics.
Grading of Bladder Cancer
Once cancer has been diagnosed, the next step is to choose the best way to treat it. To help do this, a specialist called a pathologist studies your tumor sample. They do this in a lab using a microscope to see out how different the cancer cells look from normal cells. This is called the cancer grade.
Grade: What the cancer cells look like
The grade of bladder cancer is found by looking at the cancer cells under a microscope. It's based on how much the cancer cells look like normal cells and how many cells are multiplying. The higher the grade, the more different the cells are and the more cancer cells are multiplying. High-grade cancers are more likely to grow and spread quickly. Knowing the grade can help your healthcare provider predict how fast the cancer will grow and spread. This information is used to plan your treatment.
Low grade
Low-grade (well-differentiated) cells look fairly normal compared with normal bladder cells. A few of the cells vary in size. Some of the cells are multiplying. These cancer cells grow and spread more slowly than high grade cancer cells.
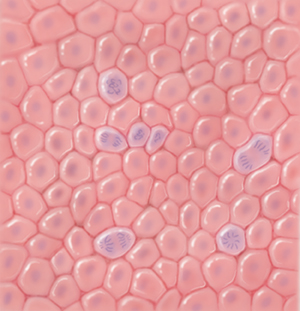 |
| Low-grade cancer cells. |
High grade
High-grade (poorly differentiated or undifferentiated) cells are abnormal looking compared with normal bladder cells. They are very uneven in shape. They vary widely in size. A lot of the cancer cells are multiplying. They grow and spread more quickly than low grade cancer cells. They may also look heaped up or loose compared to the normal pattern of bladder cells.
 |
| High-grade cancer cells. |
Online Medical Reviewer:
Jessica Gotwals RN BSN MPH
Online Medical Reviewer:
Rita Sather RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Susan K. Dempsey-Walls RN
Date Last Reviewed:
9/1/2023
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.