A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Topic IndexLibrary Index
Click a letter to see a list of conditions beginning with that letter.
Click 'Topic Index' to return to the index for the current topic.
Click 'Library Index' to return to the listing of all topics.
Your Heart’s Electrical System
The heartbeat is the rhythmic squeezing (contraction) of the heart muscle's four chambers. The four chambers are called the right atrium, the right ventricle, the left atrium, and the left ventricle. The heart muscle has a system that creates and sends electrical signals to trigger the action of these four chambers. First, an electrical signal is made in the right upper chamber of the heart. This signal tells the two upper chambers (atria) to squeeze. This moves blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). Next, the signals tell the ventricles to squeeze. This moves blood to the lungs, brain, heart, and body.
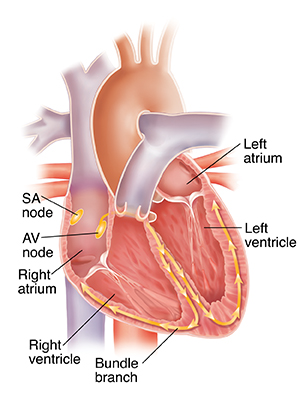
Electrical signals
Groups of specialized cells in the right atrium send out the heart’s electrical signals. These groups of cells are called nodes. The signals travel along pathways. In the ventricles, these pathways are called bundle branches.
The SA (sinoatrial) node
The SA usually sets the pace of the heartbeat. Each heartbeat is normally evenly spaced from beat to beat. It starts each beat by releasing an electrical signal. This signal tells the atria to squeeze. The resting rate for this is between 60 and 100 beats per minute. After the atria squeeze, they relax so they can fill up with blood again, until the next electrical signal comes.
The AV (atrioventricular) node
This group of specialized cells gets the electrical signals from the atria. It's like a "gatekeeper" between the atria and the ventricles. The AV node sends the signals into the ventricles after a delay. This lets the atria contract before the ventricles contract. If the sinus node fails to fire, the AV node may also kick in as a backup. It has a rate of 40 to 60 beats per minute.
The bundle branches
These branches carry the electrical signals through the ventricle walls. This causes the ventricles to squeeze and pump blood. After they squeeze, they relax so they can fill up with blood again, until the next electrical signal comes.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Marianne Fraser MSN RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Rita Sather RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Stacey Wojcik MBA BSN RN
Date Last Reviewed:
8/1/2023
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.